Health Topics
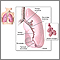
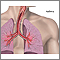
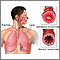
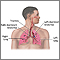
Asthma is a chronic disease that causes the airways of the lungs to swell and become narrow. It leads to breathing difficulty such as wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing.
Causes
Asthma is caused by swelling (inflammation) in the airways. An asthma attack occurs when the lining of the air passages has become swollen and the muscles surrounding the airways become tight. This narrowing reduces the amount of air that can pass through the airway.
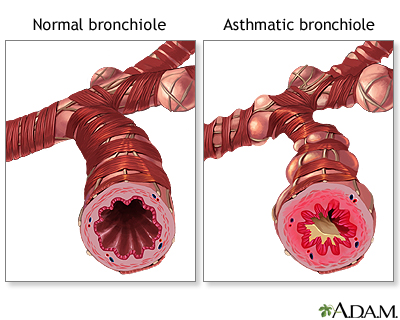
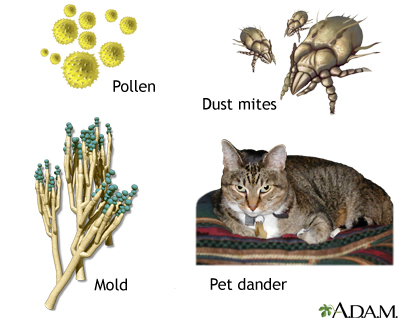
Asthma symptoms can be caused by breathing in substances called allergens or triggers, or by other causes.
Common asthma triggers include:
- Animals (pet hair or dander)
- Dust mites
- Certain medicines (such as aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs [NSAIDs])
- Changes in weather (most often cold weather)
- Chemicals in the air (pollution) or in food
- Physical activity
- Mold
- Pollen
- Respiratory infections, such as the common cold and many other viruses
- Strong emotions (stress)
- Tobacco or other inhalant that is smoked
Substances in some workplaces can also trigger asthma symptoms, leading to occupational asthma. The most common triggers are wood dust, grain dust, animal dander, fungi, or chemicals.
Many people with asthma have a personal or family history of allergies, such as hay fever (allergic rhinitis) or eczema. Others have no history of allergies.
Symptoms
Asthma symptoms vary from person to person. For example, you may have symptoms all the time or mostly during physical activity.
Most people with asthma have attacks separated by symptom-free periods. Some people have long-term shortness of breath with episodes of increased shortness of breath. Wheezing or a cough may be the main symptom.
Asthma attacks can last for minutes to days. An asthma attack may start suddenly or develop slowly over several hours or days. It may become dangerous if airflow is severely blocked.
Symptoms of asthma include:
- Cough with or without phlegm (sputum) production
- Pulling in of the skin between the ribs when breathing (intercostal retractions)
- Shortness of breath that gets worse with exercise or activity
- Whistling sound or wheezing as you breathe
- Pain or tightness in the chest
- Difficulty sleeping
- Abnormal breathing pattern (breathing out takes more than twice as long as breathing in)
Emergency symptoms that need prompt medical help include:
- Bluish color to the lips and face (cyanosis)
- Decreased level of alertness, such as severe drowsiness or confusion, during an asthma attack
- Extreme difficulty breathing
- Rapid pulse
- Severe anxiety due to shortness of breath
- Sweating
- Difficulty speaking
- Breathing temporarily stops
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will use a stethoscope to listen to your lungs. Wheezing or other asthma-related sounds may be heard. Your provider will take your medical history and ask about your symptoms.
Tests that may be ordered include:
- Allergy testing -- a skin test or a blood test to see if a person with asthma is allergic to certain substances
- Arterial blood gas -- often done in people who are having a severe asthma attack
- Chest x-ray or CT scan of the chest -- mainly to check for other conditions as asthma attacks often occur with a fully normal chest X-ray or CT scan
- Lung function tests, including peak flow measurements
Treatment
The goals of treatment are to:
- Control airway swelling
- Limit exposure to substances that may trigger your symptoms
- Help you to do normal activities without having asthma symptoms
You and your provider should work as a team to manage your asthma symptoms. Follow your provider's instructions on taking medicines, removing asthma triggers, and tracking symptoms.
MEDICINES FOR ASTHMA
Your provider may prescribe two kinds of medicines for treating your asthma:
- Long term or control medicines to help prevent attacks
- Quick-relief (rescue) medicines for use during attacks
These are also called maintenance or control medicines. They are used to prevent symptoms in people with moderate to severe asthma. You must take these medicines every day for them to work as well as possible. Take them even when you feel OK.
Some long-term medicines are breathed in (inhaled), such as steroids and long-acting beta-agonists. Others are taken by mouth (orally). Your provider will prescribe the right medicine for you.
These are also called rescue medicines. They are taken:
- For coughing, wheezing, trouble breathing, or other symptoms during an asthma attack
- Just before physical activity to help prevent asthma symptoms
Tell your provider if you are using quick-relief medicines twice a week or more. If so, your asthma may not be under control. Your provider may change the dose or your daily asthma control medicine to reduce the use of quick-relief medicines.
Quick-relief medicines include:
- Short-acting inhaled bronchodilators
- Oral corticosteroids for a severe asthma attack
A severe asthma attack requires a visit to your provider. You may also need a hospital stay. There, you will likely be given oxygen, breathing assistance, and medicines given through a vein (IV) or by a nebulizer.
ASTHMA CARE AT HOME
You can take steps to reduce the chance of asthma attacks:
- Know the asthma symptoms to watch for.
- Know how to take your peak flow reading and what it means.
- Know which triggers make your asthma worse and what to do when it happens.
- Know how to take care of your asthma before and during physical activity or exercise.
Asthma action plans are written documents for managing asthma. An asthma action plan should include:
- Instructions for taking asthma medicines when your condition is stable
- A list of asthma triggers and how to avoid them
- How to recognize when your asthma is getting worse, what to do and when to contact your provider
A peak flow meter is a simple device to measure how quickly you can move air out of your lungs.
- It can help you see if an attack is coming, sometimes even before symptoms appear. Peak flow measurements help let you know when you need to take medicine or other action.
- Peak flow values of 50% to 80% of your best results are a sign of a moderate asthma attack. Numbers below 50% are a sign of a severe attack.
Outlook (Prognosis)
There is no cure for asthma, although symptoms sometimes improve over time, particularly in children. With proper self-care and medical treatment, most people with asthma can lead a normal life.
Possible Complications
The complications of asthma can be severe, and may include:
- Death
- Decreased ability to exercise and take part in other activities
- Lack of sleep due to nighttime symptoms
- Permanent changes in the function of the lungs
- Persistent cough
- Trouble breathing that requires breathing assistance (ventilator)
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider for an appointment if asthma symptoms develop.
Contact your provider right away if:
- An asthma attack requires more medicine than recommended
- Symptoms get worse or do not improve with treatment
- You have shortness of breath while talking
- Your peak flow measurement is 50% to 80% of your personal best
Go to the emergency room or call Emergency Medical Services (EMS) right away if these symptoms occur:
- Drowsiness or confusion
- Severe shortness of breath at rest
- A peak flow measurement of less than 50% of your personal best
- Severe chest pain
- Bluish color to the lips and face
- Extreme difficulty breathing
- Rapid pulse
- Severe anxiety due to shortness of breath
Prevention
You can reduce asthma symptoms by avoiding triggers and substances that irritate the airways.
- Cover bedding with allergy-proof casings to reduce exposure to dust mites.
- Remove carpets from bedrooms and vacuum regularly.
- Use only unscented detergents and cleaning materials in the home.
- Keep humidity levels low and fix leaks to reduce the growth of organisms such as mold.
- Keep the house clean and keep food in containers and out of bedrooms. This helps reduce the possibility of cockroaches. Body parts and droppings from cockroaches can trigger asthma attacks in some people.
- If someone is allergic to an animal that cannot be removed from the home, the animal should be kept out of the bedroom. Place filtering material over the heating/air conditioning outlets in your home to trap animal dander. Change the filter in furnaces and air conditioners often.
- Eliminate tobacco smoke from the home. This is the single most important thing a family can do to help someone with asthma. Smoking outside the house is not enough. Family members and visitors who smoke outside carry smoke residue inside on their clothes and hair. This can trigger asthma symptoms. If you smoke, now is a good time to quit.
- Avoid air pollution, industrial dust, and irritating fumes as much as possible.
Alternative Names
Bronchial asthma; Wheezing - asthma - adults
Patient Instructions
- Asthma and school
- Asthma - control drugs
- Asthma in adults - what to ask the doctor
- Asthma - quick-relief drugs
- Exercise-induced asthma
- Exercising and asthma at school
- How to use a nebulizer
- How to use an inhaler - no spacer
- How to use an inhaler - with spacer
- How to use your peak flow meter
- Make peak flow a habit
- Signs of an asthma attack
- Stay away from asthma triggers
- Traveling with breathing problems
References
Boulet L-P, Godbout K. Diagnosis of asthma in adults. In: Burks AW, Holgate ST, O'Hehir RE, et al, eds. Middleton's Allergy: Principles and Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 51.
Cloutier MM, Dixon AE, Krishnan JA, Lemanske RF Jr, Pace W, Schatz M. Managing asthma in adolescents and adults: 2020 asthma guideline update from the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program. JAMA. 2020;324(22):2301-2317. PMID: 33270095 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33270095/.
Drazen JM, Bel EH. Asthma. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 75.
Liu AH, Bacharier LB, Fitzpatrick AM, Sicherer SH. Childhood asthma. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 185.
Vohra TT, Nowak RM. Asthma. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 59.
Test Your Knowledge
Review Date 1/1/2025
Updated by: Frank D. Brodkey, MD, FCCM, Associate Professor, Section of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, WI. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.