Health Topics
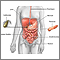
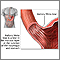
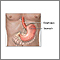
A Mallory-Weiss tear occurs in the mucous membrane of the lower part of the esophagus or upper part of the stomach, near where they join. The tear may bleed.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- Bloody stools
- Vomiting blood (bright red)
Exams and Tests
Tests may include:
- CBC, possibly showing low hematocrit
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), more likely to be done when there is active bleeding or high-risk for rebleeding.
Treatment
The tear usually heals in a few days without treatment. The tear may also be fixed by clips, electrocoagulation, or epinephrine injection that may be done during an EGD. Surgery is rarely needed. Medicines that suppress stomach acid (proton pump inhibitors) are typically given for a short time after to decrease rebleeding.
If blood loss has been large, blood transfusions may be needed. In most cases, bleeding stops without treatment within a few hours.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Repeated bleeding is uncommon and the outcome is most often good. Cirrhosis of the liver and problems with blood clotting make future bleeding episodes more likely to occur.
Possible Complications
Hemorrhage (loss of blood)
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if you begin vomiting blood or if you pass bloody stools.
Prevention
Treatments to relieve vomiting and coughing may reduce risk. Avoid excessive alcohol use.
Alternative Names
Mucosal lacerations - gastroesophageal junction
References
Falk GW, Katzka DA. Diseases of the esophagus. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 124.
Katzka DA. Esophageal disorders caused by medications, trauma, and infection. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 45.
Review Date 10/30/2024
Updated by: Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Gastroenterologist, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.