Health Topics
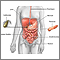
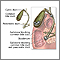
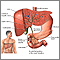
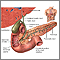
Choledocholithiasis means there is at least one gallstone in the common bile duct. The stone may be made up of bile pigments or calcium and cholesterol salts and are called common bile duct stones.
Causes
About 1 in 7 people with gallstones will develop stones in the common bile duct. This is the small tube that carries bile from the gallbladder to the intestine.
Risk factors include a history of gallstones. However, choledocholithiasis can occur in people who have had their gallbladder removed.
Symptoms
Often, there are no symptoms unless the stone blocks the common bile duct. Symptoms may include:
- Pain in the right upper or middle upper abdomen for at least 30 minutes. The pain may be constant and intense. It can be mild or severe. The pain may radiate to the back in the area of the right shoulder blade.
- Fever.
- Yellowing of skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice).
- Loss of appetite.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Clay-colored stools.
Exams and Tests
Tests that show the location of stones in the bile duct include the following:
- Abdominal CT scan
- Abdominal ultrasound
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
- Endoscopic ultrasound
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) -- this is the most accurate non-invasive test to look for a common bile duct stone
- Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiogram (PTC)
Your health care provider may order the following blood tests:
- Bilirubin
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Liver function tests
- Pancreatic enzymes (amylase or lipase)
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to relieve the blockage of the common bile duct.
Treatment may involve:
- Surgery to remove the gallbladder and stones
- ERCP and a procedure called a sphincterotomy, which makes a surgical cut into the muscle in the common bile duct to allow stones to pass or be removed
Outlook (Prognosis)
Blockage and infection caused by stones in the biliary tract can be life threatening. Most of the time, the outcome is good if the problem is detected and treated early.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Biliary cirrhosis
- Cholangitis
- Pancreatitis
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You develop abdominal pain, with or without fever, and there is no known cause
- You develop jaundice
- You have other symptoms of choledocholithiasis
Alternative Names
Gallstone in the bile duct; Bile duct stone; Common bile duct stone
References
Fogel EL, Sherman S. Diseases of the gallbladder and bile ducts. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 141.
Radkani P, Hawksworth J, Fishbein T. Biliary system. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:chap 55.
Wang D Q-H, Afdhal NH. Gallstone disease. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 65.
Review Date 4/21/2025
Updated by: Todd Eisner, MD, Private practice specializing in Gastroenterology in Boca Raton and Delray Beach, Florida at Gastroenterology Consultants of Boca Raton. Affiliate Assistant Professor, Florida Atlantic University School of Medicine. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.