Health Topics
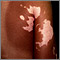
Vitiligo is a skin condition in which there is a loss of color (pigment) from areas of skin. This results in uneven white patches that have no pigment, but the skin feels normal.
Causes
Vitiligo occurs when immune cells destroy the cells that make brown pigment (melanocytes). This destruction is thought to be due to an autoimmune problem. An autoimmune disorder occurs when the body's immune system, which normally protects the body from infection, attacks and destroys healthy body tissue instead. The exact cause of vitiligo is unknown.
Vitiligo may appear at any age. There is an increased rate of the condition in some families.
Vitiligo is associated with other autoimmune diseases:
- Addison disease (disorder that occurs when the adrenal glands do not produce enough hormones)
- Thyroid disease
- Pernicious anemia (decrease in red blood cells that occurs when the intestines cannot properly absorb vitamin B12)
- Type 1 diabetes
Symptoms
Flat areas of normal-feeling skin without any pigment appear suddenly or gradually. These areas have a darker border. The edges are well defined, but irregular.
Vitiligo most often affects the face, elbows and knees, back of the hands and feet, and genitals. It affects both sides of the body equally.
Vitiligo is more noticeable in darker-skinned people because of the contrast of white patches against dark skin.
No other skin changes occur.
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider can examine your skin to confirm the diagnosis.
Sometimes, the provider uses a Wood lamp. This is a handheld ultraviolet light that causes the areas of skin with less pigment to glow bright white.
In some cases, a skin biopsy may be needed to check for other causes of pigment loss. Your provider may also perform blood tests to check the levels of thyroid or other hormones, glucose level, and vitamin B12 to check for other associated disorders.
Treatment
Vitiligo is difficult to treat. Early treatment options include the following:
- Phototherapy, a medical procedure in which your skin is carefully exposed to limited amounts of ultraviolet light. Phototherapy may be given alone, or after you take a medicine that makes your skin sensitive to light. A dermatologist performs this treatment.
- Certain lasers may help the skin repigment.
- Medicines applied to the skin, such as corticosteroid creams or ointments, immunosuppressant creams or ointments such as pimecrolimus (Elidel) and tacrolimus (Protopic), or topical medicines such as methoxsalen (Oxsoralen) may also help.
Skin may be moved (grafted) from normally pigmented areas and placed onto areas where there is pigment loss.
Several cover-up makeups or skin dyes can mask vitiligo. Ask your provider for the names of these products.
In extreme cases when most of the body is affected, the remaining skin that still has pigment may be depigmented, or bleached. This is a permanent change that is used as a last option.
It is important to remember that skin without pigment is at greater risk for sun damage. Be sure to apply a broad-spectrum (UVA and UVB), high-SPF sunscreen or sunblock. Sunscreen can also be helpful for making the condition less noticeable, because unaffected skin may not darken in the sun. Use other safeguards against sun exposure, such as wearing a hat with a broad rim and long sleeve shirt and pants.
Support Groups
More information and support for people with vitiligo condition and their families can be found at:
- Vitiligo Support International - vitiligosupport.org
Outlook (Prognosis)
The course of vitiligo varies and is unpredictable. Some areas may regain normal pigment (coloring), but other new areas of pigment loss may appear. Skin that is repigmented may be slightly lighter or darker than the surrounding skin. Pigment loss may get worse over time.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider for an appointment if areas of your skin lose their coloring for no reason (for example, there was no injury to the skin).
Alternative Names
Autoimmune disorder - vitiligo
References
Dinulos JGH. Light-related diseases and disorders of pigmentation. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 19.
Patterson JW. Disorders of pigmentation. In: Patterson JW, ed. Weedon's Skin Pathology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 11.
Seneschal J, Passeron T, Torrelo A, Ortonne J-P. Vitiligo and other disorders of hypopigmentation. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 66.
Review Date 5/28/2024
Updated by: Ramin Fathi, MD, FAAD, Director, Phoenix Surgical Dermatology Group, Phoenix, AZ. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.