Health Topics
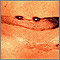
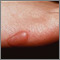
A keloid is a growth of extra scar tissue. It occurs where the skin has healed after an injury.
Causes
Keloids can form after skin injuries from:
- Acne
- Burns
- Chickenpox
- Ear or body piercing
- Minor scratches
- Cuts from surgery or trauma
- Vaccination sites
Keloids are most common in people younger than 30. Black people, Asians, and Hispanics are more prone to developing keloids. Keloids often run in families. Sometimes, a person may not recall what injury caused a keloid to form.
Symptoms
A keloid may be:
- Flesh-colored, red, or pink
- Located over the site of a wound or injury
- Lumpy or ridged
- Tender and itchy
- Irritated from friction such as rubbing on clothing
A keloid will tan darker than the skin around it if exposed to the sun during the first year after it forms. The darker color may not go away.
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will look at your skin to see if you have a keloid. A skin biopsy may be done to check for other types of skin growths (tumors).
Treatment
Keloids often do not need treatment. If the keloid bothers you, discuss your concern with a skin specialist (dermatologist). Your dermatologist may recommend these treatments to reduce the size of the keloid:
- Corticosteroid injections
- Freezing (cryotherapy)
- Laser treatments
- Radiation
- Surgical removal
- Silicone gel or patches
These treatments, especially surgery, sometimes cause the keloid scar to become larger.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Keloids usually are not harmful to your health, but they may affect how you look.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You develop keloids and want to have them removed or reduced
- You develop new symptoms
Prevention
When you are in the sun:
- Cover a keloid that is forming with a patch or adhesive bandage.
- Use sunblock.
Continue to follow these steps for at least 6 months after injury or surgery for adults. Children may need up to 18 months of prevention.
Imiquimod cream may help prevent keloids from forming after surgery. The cream may also prevent keloids from returning after they are removed.
Alternative Names
Keloid scar; Scar - keloid
References
Dinulos JGH. Benign skin tumors. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 20.
Machan S, Molina-Ruiz AM, Requena L. Dermal hypertrophies. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 98.
Patterson JW. Disorders of collagen. In: Patterson JW, ed. Weedon's Skin Pathology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 12.
Review Date 10/13/2024
Updated by: Ramin Fathi, MD, FAAD, Director, Phoenix Surgical Dermatology Group, Phoenix, AZ. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.