Health Topics
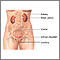
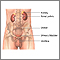
Bladder stones are hard buildups of minerals. These form in the urinary bladder.
Causes
Bladder stones are most often caused by another urinary system problem, such as:
- Bladder diverticulum
- Blockage at the base of the bladder
- Enlarged prostate (BPH)
- Neurogenic bladder
- Urinary tract infection (UTI)
- Incomplete emptying of the bladder
- Foreign objects in the bladder
Almost all bladder stones occur in men. Bladder stones are much less common than kidney stones.
Bladder stones may occur when urine in the bladder is concentrated. Materials in the urine form crystals. These may also result from foreign objects in the bladder.
Symptoms
Symptoms occur when the stone irritates the lining of the bladder. The stones may also block the flow of urine from the bladder.
Symptoms can include:
- Abdominal pain, pressure
- Abnormally colored or dark-colored urine
- Blood in the urine
- Difficulty urinating
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Inability to urinate except in certain positions
- Interruption of the urine stream
- Pain, discomfort in the penis
- Signs of UTI (such as fever, pain when urinating, and need to urinate often)
Loss of urine control may also occur with bladder stones.
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam. This will also include a rectal exam. The exam may reveal an enlarged prostate in men or other problems.
The following tests may be done:
- Bladder or pelvis x-ray
- Cystoscopy
- Urinalysis
- Urine culture (clean catch)
- Abdominal ultrasound or CT scan
Treatment
You may be able to help small stones pass on their own. Drinking 6 to 8 glasses of water or more per day will increase urination.
Your doctor (urologist) may remove stones that do not pass using a cystoscope. A small telescope will be passed through the urethra into the bladder. A laser or other device will be used to break up the stones and the pieces will be removed. Some stones may need to be removed using open surgery.
Medicines are rarely used to dissolve the stones.
Causes of bladder stones should be treated. Most commonly, bladder stones are seen with BPH or blockage at the base of the bladder. You may need surgery to remove the inside part of the prostate or to repair the bladder.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most bladder stones pass on their own or can be removed. They do not cause permanent damage to the bladder. They may come back if the cause is not corrected.
Left untreated, stones may cause repeated UTIs. This can also cause permanent damage to the bladder or kidneys.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of bladder stones.
Prevention
Prompt treatment of a UTI or other urinary tract conditions may help prevent bladder stones.
Alternative Names
Stones - bladder; Urinary tract stones; Bladder calculi
References
Ganpule AP, Desai MR. Lower urinary tract calculi. In: Partin AW, Dmochowski RR, Kavoussi LR, Peters CA, eds. Campbell-Walsh-Wein Urology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 95.
Germann CA. Urologic disorders. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 85.
Review Date 5/17/2024
Updated by: Sovrin M. Shah, MD, Associate Professor, Department of Urology, The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.