Health Topics
This article discusses vaginal bleeding that occurs between a woman's monthly menstrual periods. Such bleeding may be called "intermenstrual bleeding."
Related topics include:
- Dysfunctional uterine bleeding
- Heavy, prolonged, or irregular menstrual periods
Considerations
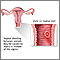
Normal menstrual flow lasts about 5 days. It produces a total blood loss of 30 to 80 mL (about 2 to 5 tablespoons), and occurs normally every 21 to 35 days.
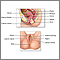
Vaginal bleeding that occurs between periods or after menopause can be caused by various problems. Most are benign and can be easily treated. Sometimes, vaginal bleeding may be due to cancer or pre-cancer. Therefore, any unusual bleeding should be evaluated right away. The risk for cancer increases to about 10% in women with postmenopausal bleeding.
Make sure that bleeding is coming from the vagina and is not from the rectum or the urine. Inserting a tampon into the vagina will confirm the vagina, cervix, or uterus as the source of bleeding.
A careful exam by your health care provider is most often the best way to find the source of the bleeding. This exam can be done even while you are bleeding.
Causes
Causes may include:
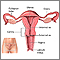
- Uterine fibroids or cervical or uterine polyps
- Changes in hormone levels
- Inflammation or infection of the cervix (cervicitis) or uterus (endometritis)
- Injury or disease of the vaginal opening (caused by intercourse, trauma, infection, polyp, genital warts, ulcer, or varicose veins)
- Intrauterine device (IUD) use, (may cause occasional spotting)
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Miscarriage
- Other pregnancy complications
- Vaginal dryness due to lack of estrogen after menopause
- Stress
- Using hormonal birth control irregularly (such as stopping and starting or skipping birth control pills, patches, or estrogen rings)
- Underactive thyroid (low thyroid function)
- Use of blood thinners (anticoagulants)
- Cancer or pre-cancer of the cervix, uterus, or (very rarely) fallopian tube
- Pelvic exam, cervical biopsy, endometrial biopsy, or other procedures
Home Care
Contact your provider right away if bleeding is very heavy.
Keep track of the number of pads or tampons used over time so that the amount of bleeding can be determined. Uterine blood loss can be estimated by keeping track of how frequently a pad or tampon is soaked and how often one needs to be changed.
If possible, aspirin should be avoided, as it may prolong bleeding. However, NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), such as ibuprofen can be used to minimize bleeding and cramping.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You are pregnant.
- There is any unexplained bleeding between periods.
- There is any bleeding after menopause.
- There is heavy bleeding with periods.
- Abnormal bleeding is accompanied by other symptoms, such as pelvic pain, fatigue, dizziness.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will perform a physical exam and ask questions about your medical history. The physical exam will include a pelvic exam.
Questions about the bleeding may include:
- When does the bleeding occur and how long does it last?
- How heavy is the bleeding?
- Do you have cramps too?
- Are there things that make the bleeding worse?
- Is there anything that prevents it or relieves it?
- Do you have any other symptoms such as abdominal pain, bruising, pain when urinating, or blood in urine or stools?
Tests that may be done include:
- Blood tests to check thyroid and ovarian function
- Cervical cultures to check for a sexually transmitted infection
- Colposcopy and cervical biopsy
- Endometrial (uterine) biopsy
- Pap smear
- Pelvic ultrasound
- Saline infusion sonohysterogram
- Hysterosonogram
- Hysteroscopy
- Pregnancy test
Most causes of intermenstrual bleeding are easily treatable. The problem can most often be diagnosed without too much discomfort. Therefore, it is important not to delay in having this problem evaluated by your provider.
Alternative Names
Bleeding between periods; Intermenstrual bleeding; Spotting; Metrorrhagia
References
Bulun SE, Babayev E. Physiology and pathology of the female reproductive axis. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Rosen CJ, Kopp PA, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 15th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 15.
Ellenson LH, Roberts DJ. The female genital tract. In: Aster JC, Abbas AK, Kumar AK, Debnath J, Das A, eds. Robbins, Cotran & Kumar Pathologic Basis of Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2026:chap 22.
Ryntz T, Lobo RA. Abnormal uterine bleeding: etiology and management of acute and chronic excessive bleeding. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 26.
Review Date 5/22/2025
Updated by: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.