Health Topics
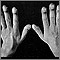
Clubbing is changes in the areas under and around the toenails and fingernails that occur with some disorders. The nails may also show changes.
Considerations
Common symptoms of clubbing:
- The nail beds soften. The nails may seem to float instead of being firmly attached.
- The nails form a sharper angle with the cuticle.
- The last part of the finger may appear large or bulging. It may also be warm and red.
- The nail curves downward so it looks like the round part of an upside-down spoon.
Clubbing can develop quickly, often within weeks. It also can go away quickly when its cause is treated.
Causes
Lung cancer is the most common cause of clubbing. Clubbing often occurs in heart and lung diseases that reduce the amount of oxygen in the blood. These may include:
- Heart defects that are present at birth (congenital)
- Chronic lung infections that occur in people with bronchiectasis, cystic fibrosis, or lung abscess
- Infection of the lining of the heart chambers and heart valves (infectious endocarditis). This can be caused by bacteria, fungi, or other infectious substances
- Lung disorders in which the deep lung tissues become swollen and then scarred (interstitial lung disease)
Other causes of clubbing:
- Celiac disease
- Cirrhosis of the liver and other liver diseases
- Dysentery
- Graves disease
- Overactive thyroid gland
- Other types of cancer, including liver, gastrointestinal, Hodgkin lymphoma
When to Contact a Medical Professional
If you notice clubbing, contact your health care provider.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
A person with clubbing often has symptoms of another condition. Diagnosing that condition is based on:
- Family history
- Medical history
- Physical exam that looks at the lungs and chest
The provider may ask questions such as:
- Do you have any trouble breathing?
- Do you have clubbing of the fingers, toes, or both?
- When did you first notice this? Do you think it is getting worse?
- Does your skin ever have a blue color (cyanosis)?
- What other symptoms do you have?
The following tests may be done:
- Arterial blood gas
- Chest CT scan
- Chest x-ray
- Echocardiogram
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Pulmonary function tests
There is no treatment for the clubbing itself. The cause of clubbing can be treated, however.
Alternative Names
Clubbing
Images
References
Drake WM, Chowdhury TA. General patient examination and differential diagnosis. In: Glynn M, Drake WM, eds. Hutchison's Clinical Methods. 25th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 2.
Fajardo E, Davis JL. History and physical examination. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray & Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 18.
Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al. Cyanotic congenital heart disease: lesions associated with decreased pulmonary blood flow. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 479.
Review Date 4/10/2025
Updated by: Allen J. Blaivas, DO, Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine, VA New Jersey Health Care System, Clinical Assistant Professor, Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, East Orange, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.