Health Topics
Amylase is an enzyme that helps digest carbohydrates. It is made primarily in the pancreas and the glands that make saliva, and can be found at low levels in other parts of the body. When the pancreas is diseased or inflamed, it releases increased amounts of amylase into the blood.
A test can be done to measure the level of this enzyme in your blood.
Amylase may also be measured with a urine amylase test.
How the Test is Performed
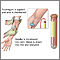
A blood sample is taken from a vein.
How to Prepare for the Test
No special preparation is needed. However, you should avoid alcohol before the test. Your health care provider may ask you to stop taking medicines that may affect the test. Do not stop taking any medicines without first talking to your provider.
Medicines that can increase amylase measurements include:
- Asparaginase
- Aspirin
- Birth control pills
- Cholinergic medicines
- Ethacrynic acid
- Methyldopa
- Opiates (codeine, meperidine, and morphine)
- Thiazide diuretics
How the Test will Feel
You may feel slight pain or a sting when the needle is inserted to draw blood. Afterward, there may be some throbbing.
Why the Test is Performed
This test is most often used to diagnose or monitor acute pancreatitis. It may also detect some digestive tract problems or salivary gland inflammation.
The test may also be done for the following conditions:
Normal Results
The normal range is 40 to 140 units per liter (U/L) or 0.67 to 2.34 micro-katal/liter (µkat/L).
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some laboratories use different measurement methods. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Increased blood amylase level may occur due to:
- Acute pancreatitis
- Cancer of the pancreas, ovaries, or lungs
- Cholecystitis
- Infection of the salivary glands (such as mumps) or a blockage of the salivary gland duct
- Intestinal blockage
- Macroamylasemia
- Pancreatic or bile duct blockage
- Perforated ulcer
- Tubal pregnancy (may have burst open)
- Viral hepatitis
Decreased amylase level may occur due to:
- Bone fracture
- Congestive heart failure
- Damage to the pancreas with pancreatic scarring
- Gastrointestinal cancer
- Pregnancy
Risks
Slight risks from having blood drawn may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
- Hematoma (blood accumulating under the skin)
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
Alternative Names
Pancreatitis - blood amylase
Images
References
Forsmark CE. Pancreatitis. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 135.
Siddiqi HA, Rabinowitz S, Axiotis CA. Laboratory diagnosis of gastrointestinal and pancreatic disorders. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 23.
Tenner S, Vege SS, Sheth SG, et al. American College of Gastroenterology Guidelines: Management of acute pancreatitis. Am J Gastro 2024;119(3):419-437. PMID: 38857482 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38857482/.
Vege SS. Acute pancreatitis. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 58.
Review Date 1/1/2025
Updated by: Frank D. Brodkey, MD, FCCM, Associate Professor, Section of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, WI. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.