Health Topics
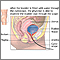
Cystoscopy is a surgical procedure. This is done to see the inside of the bladder and urethra using a thin, lighted tube.
How the Test is Performed
Cystoscopy is done with a cystoscope. This is a special tube with a small camera on the end (endoscope). There are two types of cystoscopes:
- Standard, rigid cystoscope
- Flexible cystoscope
The tube can be inserted in different ways. However, the test is the same either way. The type of cystoscope your doctor (urologist) will use depends on the purpose of the exam.
The procedure will take about 5 to 20 minutes. The urethra is cleansed. A numbing medicine is applied to the skin lining the inside of the urethra. This is done without needles. The scope is then inserted through the urethra into the bladder.
Water or salt water (saline) flows through the tube to fill the bladder. As this occurs, you may be asked to describe the feeling. Your answer will give some information about your condition.
As fluid fills the bladder, it stretches the bladder wall. This lets your doctor see the entire bladder wall. You will feel the need to urinate when the bladder is full. However, the bladder must stay full until the exam is finished.
If any tissue looks abnormal, a small sample can be taken (biopsy) through the tube. This sample will be sent to a lab to be tested.
How to Prepare for the Test
Ask your doctor if you should stop taking any medicines that could thin your blood.
The procedure may be done under anesthesia in a hospital or surgery center. In that case, you will need to have someone take you home afterward.
How the Test will Feel
You may feel slight discomfort when the tube is passed through the urethra into the bladder. You will feel an uncomfortable, strong need to urinate when your bladder is full.
You may feel a quick pinch if a biopsy is taken. After the tube is removed, the urethra may be sore. You may have blood in the urine and a burning sensation during urination for a day or two.
Why the Test is Performed
The test is done to:
- Check for cancer of the bladder or urethra
- Diagnose the cause of blood in the urine
- Diagnose the cause of problems passing urine
- Diagnose the cause of repeated bladder infections
- Help determine the cause of pain during urination
Normal Results
The bladder wall should look smooth. The bladder should be of normal size, shape, and position. There should be no blockages, growths, or stones.
What Abnormal Results Mean
The abnormal results could indicate:
- Bladder cancer
- Bladder stones (calculi)
- Bladder wall decompression
- Chronic urethritis or cystitis
- Scarring of the urethra (called a stricture)
- Congenital (present at birth) abnormality
- Cysts
- Diverticula of the bladder or urethra
- Foreign material in the bladder or urethra
Some other possible diagnoses may be:
- Irritable bladder
- Polyps
- Prostate problems, such as bleeding, enlargement, or blockage
- Traumatic injury of the bladder and urethra
- Ulcer
- Urethral strictures
Risks
There is a slight risk for excess bleeding when a biopsy is taken.
Other risks include:
- Bladder infection
- Rupture of the bladder wall
Considerations
Drink 4 to 6 glasses of water per day after the procedure.
You may notice a small amount of blood in your urine after this procedure. If the bleeding continues after you urinate 3 times, contact your doctor.
Contact your doctor if you develop any of these signs of infection:
- Chills
- Fever
- Pain
- Reduced urine output
Alternative Names
Cystourethroscopy; Endoscopy of the bladder
Images
References
Duty BD, Conlin MJ. Principles of urologic endoscopy. In: Partin AW, Dmochowski RR, Kavoussi LR, Peters CA, eds. Campbell-Walsh-Wein Urology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 13.
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases website. Cystoscopy & ureteroscopy. www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diagnostic-tests/cystoscopy-ureteroscopy. Updated July 2021. Accessed June 27, 2024.
Taylor JM, Smith TG, Coburn M. Urologic surgery. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 74.
Review Date 5/17/2024
Updated by: Sovrin M. Shah, MD, Associate Professor, Department of Urology, The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.