Health Topics
Aging changes in the female reproductive system result mainly from changing hormone levels. One clear sign of aging occurs when your menstrual periods stop permanently. This is known as menopause.
The time before menopause is called perimenopause. It may begin several years before your last menstrual period. Signs of perimenopause include:
- More frequent periods at first, and then occasional missed periods
- Periods that are longer or shorter
- Changes in the amount of menstrual flow
Eventually your periods will become much less frequent, until they stop completely.
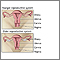
Along with changes in your periods, physical changes in your reproductive tract occur as well.
AGING CHANGES AND THEIR EFFECTS
Menopause is a normal part of a woman's aging process. Most women experience menopause around age 50, though it can occur before that age. The usual age range is 45 to 55.
With menopause:
- The ovaries stop making the hormones estrogen and progesterone.
- The ovaries also stop releasing eggs (ova, oocytes). After menopause, you can no longer become pregnant.
- Your menstrual periods stop. You know you have gone through menopause after you have had no periods for 1 year. You should continue to use a birth control method until you have gone a whole year without a period. Any bleeding that occurs more than 1 year after your last period is not normal and should be checked by your health care provider.
As hormone levels fall, other changes occur in the reproductive system, including:
- Vaginal walls become thinner, dryer, less elastic, and possibly irritated. Sometimes sex becomes painful due to these vaginal changes.
- Your risk for vaginal yeast infections increases.
- The external genital tissue decreases and thins, and can become irritated.
Other common changes include:
- Menopause symptoms such as hot flashes, moodiness, headaches, and trouble sleeping, which can persist for years
- Problems with short-term memory
- Decrease in breast tissue
- Lower sex drive (libido) and sexual response
- Increased risk for bone loss (may lead to osteoporosis)
- Urinary system changes, such as frequency and urgency of urination and increased risk for urinary tract infection
- Loss of tone in the pubic muscles, resulting in the vagina, uterus, or urinary bladder falling out of position (prolapse)
MANAGING CHANGES
Hormone therapy with estrogen or progesterone, alone or in combination, may help menopause symptoms such as hot flashes or vaginal dryness and pain with intercourse. Most women who have a uterus will require progesterone as well as estrogen. Women without a uterus may take estrogen only. Hormone therapy has risks, so it is not for every woman. Discuss the risks and benefits of hormone therapy with your provider.
To help manage problems such as painful sexual intercourse, use a lubricant during sexual intercourse. Vaginal moisturizers are available without a prescription. These can help with vaginal and vulvar discomfort due to the drying and thinning of tissues. Applying topical estrogen inside the vagina may help thicken the vaginal tissues and increase moisture and sensitivity. Your provider can tell you if any of these measures is right for you.
Getting regular exercise, eating healthy foods, and staying involved in activities with friends and loved ones can help the aging process go more smoothly.
OTHER CHANGES
Other aging changes to expect:
Images
References
Aleksic S, Bartke A, Lamberts SWJ, Milman S. Endocrine function and aging. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Rosen CJ, Kopp PA, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 15th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 26.
Lobo RA. Menopause and care of the mature woman: endocrinology, consequences of estrogen deficiency, effects of hormone therapy, and other treatment options. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 14.
Santoro N, Neal-Perry G. Menopause. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 222.
Review Date 10/15/2024
Updated by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Professor Emeritus, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.