Health Topics
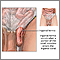
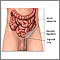
Inguinal hernia repair is surgery to repair a hernia in your groin. A hernia is tissue that bulges out of a weak spot in the abdominal wall. Your intestine may bulge out through this weakened area.
Description
During surgery to repair the hernia, the bulging tissue is pushed back into your abdomen. Your abdominal wall is strengthened and supported with sutures (stitches), and often mesh. This repair can be done with open or laparoscopic surgery. You and your surgeon can discuss which type of surgery is right for you.
Your surgeon will decide which kind of anesthesia you will receive:
- General anesthesia is medicine that keeps you asleep and pain-free.
- Regional anesthesia, which numbs you from the waist to your feet.
- Local anesthesia and medicine to relax you.
In open surgery:
- Your surgeon makes a cut near the hernia.
- The hernia is located and separated from the tissues around it. The hernia sac is removed or the hernia is gently pushed back into your abdomen.
- Your surgeon then closes your weakened abdominal muscles with stitches.
- Often a piece of mesh is also sewn into place to strengthen your abdominal wall. This repairs the weakness in the wall of your abdomen.
- At the end of the repair, the cut is stitched, stapled or glued.
In laparoscopic surgery:
- The surgeon makes three to five small cuts in your lower belly.
- A medical device called a laparoscope is inserted through one of the cuts. The scope is a thin, lighted tube with a camera on the end. It lets your surgeon see inside your belly.
- A harmless gas is pumped into your belly to expand the space. This gives your surgeon more room to see and work.
- Other tools are inserted through the other cuts. Your surgeon uses these tools to repair the hernia.
- The same repair will be done as the repair in open surgery, including mesh placement.
- At the end of the repair, the scope and other tools are removed. The cuts are stitched.
Why the Procedure is Performed
Your health care provider may suggest hernia surgery if you have pain or your hernia bothers you during your everyday activities. If the hernia is small and not causing any symptoms, you may not need surgery. However, these hernias most often do not go away on their own, tend to get larger, and a good number end up needing surgery.
Sometimes the intestine can be trapped inside the hernia. This is called an incarcerated or strangulated hernia. It can cut off blood supply to the intestines. This can be life threatening. If this happens, you would need emergency surgery.
Risks
Risks for anesthesia and surgery in general are:
- Reactions to medicines
- Breathing problems
- Bleeding, blood clots, or infection
- Nausea and vomiting
Risks for this surgery are:
- Damage to other blood vessels or organs
- Damage to the nerves
- Damage to the testicles if a blood vessel connected to them is harmed
- Long-term pain in the cut area
- Return of the hernia
Before the Procedure
Tell your surgeon or nurse if:
- You are or could be pregnant.
- You are taking any medicines, including medicines, drugs, supplements, or herbs you bought without a prescription.
Planning for your surgery:
- If you have diabetes, heart disease, or other medical conditions, your surgeon may ask you to see the provider who treats you for these conditions.
- If you smoke, it's important to cut back or quit. Smoking can slow healing and increase the risk for blood clots. Ask your provider for help quitting smoking.
- If needed, prepare your home to make it easier to recover after surgery.
- Ask your surgeon if you need to arrange to have someone drive you home after your surgery.
During the week before your surgery:
- You may be asked to temporarily stop taking medicines that keep your blood from clotting. These medicines are called blood thinners. This includes over-the-counter medicines and supplements such as aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn), and vitamin E. Many prescription medicines are also blood thinners.
- Ask your surgeon which medicines you should still take on the day of surgery.
- Let your surgeon know about any illness you may have before your surgery. This includes COVID-19, a cold, flu, fever, herpes breakout, or other illness. If you do get sick, your surgery may need to be postponed.
On the day of surgery:
- Follow instructions about when to stop eating and drinking.
- Take the medicines your surgeon told you to take with a small sip of water.
- Arrive at the hospital on time.
After the Procedure
Most people are able to get out of bed an hour or so after this surgery. Most can go home the same day, but some may need to stay in the hospital overnight.
Some men may have problems passing urine after hernia surgery. If you have problems urinating, you may need a catheter. This is a thin flexible tube that is inserted into your bladder for a short time to drain urine.
Following instructions about how active you can be while recovering. This may include:
- Returning to light activities soon after going home, but avoiding strenuous activities and heavy lifting for a few weeks.
- Avoiding activities that can increase pressure in the groin and belly. Move slowly from a lying to a seated position.
- Drinking plenty of fluids and eating lots of fiber to prevent constipation.
Follow any other self-care instructions to help speed your recovery.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outcome of this surgery is usually very good. In some people, the hernia returns.
Alternative Names
Herniorrhaphy; Hernioplasty - inguinal
Patient Instructions
References
Poulose BK, Carbonell AM, Rosen MJ. Hernias. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:chap 45.
Wiseman JE, Adrales GL. Management of inguinal hernia. In: Cameron J, ed. Current Surgical Therapy. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:663-667.
Review Date 1/21/2025
Updated by: Jonas DeMuro, MD, Diplomate of the American Board of Surgery with added Qualifications in Surgical Critical Care, Assistant Professor of Surgery, Renaissance School of Medicine, Stony Brook, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.