Health Topics
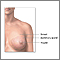
Subareolar abscess is an abscess on the areolar gland. The areolar gland is located in the breast under or below the areola (colored area around the nipple).
Causes
Subareolar abscess is caused by a blockage of the small glands or ducts below the skin of the areola. This blockage leads to infection of the glands.
This is an uncommon problem. It affects younger or middle-aged women who are not breastfeeding. Risk factors include:
- Diabetes
- Nipple piercing
- Smoking
Symptoms
Symptoms of an areolar abscess are:
- Swollen, tender lump beneath the areolar area, with swelling and warmth of the skin over it
- Drainage and possible pus from this lump
- Fever and chills
- General ill feeling or fatigue
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a breast exam. Sometimes an ultrasound or other imaging test of the breast is recommended. A blood count and a culture of the abscess, if drained, may be ordered.
Treatment
Subareolar abscesses are treated with antibiotics and by opening and draining the infected tissue. This can be done in a doctor's office with local numbing medicine. If the abscess returns, the affected glands should be surgically removed. The abscess can also be drained using a sterile needle. This is often done under ultrasound guidance.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outlook is good after the abscess is drained.
Possible Complications
Subareolar abscess may return until the affected gland is surgically removed. Any infection in a female who is not nursing has the potential to be due to a rare form of breast cancer. You may need to have a biopsy or other tests if standard treatment fails.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you develop a painful lump under your nipple or areola. It is very important to have your provider evaluate any breast mass.
Alternative Names
Abscess - areolar gland; Areolar gland abscess; Breast abscess - subareolar
References
Klimberg VS, Hunt KK. Diseases of the breast. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:chap 35.
Matalkah AM, Grobmyer SR. Mastitis and breast abscess. In: Klimberg VS, Gradishar WJ, Bland KI, Korourian S, White J, Copeland EM, eds. Bland and Copeland's The Breast: Comprehensive Management of Benign and Malignant Diseases. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 15.
Mohsin SK, Dabbs DJ. Infections of the breast. In: Dabbs DJ, ed. Breast Pathology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 3.
Review Date 10/17/2024
Updated by: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.