Health Topics
Sunken fontanelles are an obvious curving inward of the "soft spot" in an infant's head.
Considerations
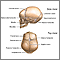
The skull is made up of many bones. There are 8 bones in the skull itself and 14 bones in the face area. They join together to form a solid, bony cavity that protects and supports the brain. The areas where the bones join together are called the sutures.
The bones are not joined together firmly at birth. This allows the head to change shape to help it pass through the birth canal. The sutures gradually gain minerals and harden, firmly joining the skull bones together. This process is called ossification.
In an infant, the space where 2 sutures join forms a membrane-covered "soft spot" called a fontanelle (fontanel). The fontanelles allow the brain and skull to grow during an infant's first year.
There are normally several fontanelles on a newborn's skull. They are located mainly at the top, back, and sides of the head. Like the sutures, fontanelles harden over time and become closed, solid, bony areas.
- The fontanelle in the back of the head (posterior fontanelle) most often closes by age 1 to 2 months.
- The fontanelle at the top of the head (anterior fontanelle) most often closes within 7 to 19 months.
The fontanelles should feel firm and should curve inward slightly to the touch. A noticeably sunken fontanelle is a sign that the infant does not have enough fluid in their body.
Causes
Reasons a child may have sunken fontanelles include:
- Dehydration (not enough fluid in the body)
- Malnutrition
When to Contact a Medical Professional
A sunken fontanelle can be a medical emergency. A health care provider should check the infant right away.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
The provider will perform a physical exam and ask questions about the child's symptoms and medical history, such as:
- When did you first notice that the fontanelle looked sunken?
- How severe is it? How would you describe it?
- Which "soft spots" are affected?
- What other symptoms are present?
- Has the baby been ill, especially with vomiting, diarrhea, or excessive sweating?
- Is the skin turgor poor?
- Is the baby thirsty?
- Is the baby alert?
- Are the baby's eyes dry?
- Is the baby's mouth moist?
Tests may include:
- Blood chemistries
- CBC
- Urinalysis
- Tests to check the baby's nutritional status
You might be referred to a health care facility that can provide intravenous (IV) fluids if the sunken fontanelle is caused by dehydration.
Alternative Names
Sunken fontanelles; Soft spot - sunken
References
Parga-Belinkie JJ. The newborn infant. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 115.
Wright CJ, Posencheg MA, Seri I. Fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base balance. In: Gleason CA, Sawyer T, eds. Avery's Diseases of the Newborn. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 20.
Review Date 1/17/2025
Updated by: Charles I. Schwartz, MD, FAAP, Clinical Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, General Pediatrician at PennCare for Kids, Phoenixville, PA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.