Health Topics
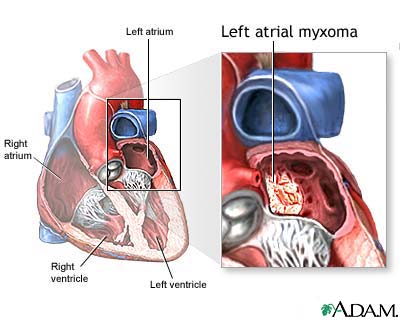
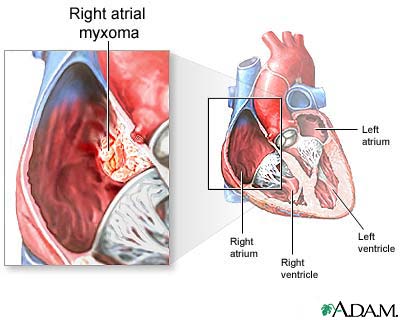
An atrial myxoma is a noncancerous tumor in the upper left or right side of the heart. It most often grows on the wall that separates the two sides of the heart. This wall is called the atrial septum.
Causes
A myxoma is a primary heart (cardiac) tumor. This means that the tumor started within the heart. Most heart tumors start somewhere else.
Primary cardiac tumors such as myxomas are rare. About 75% of myxomas occur in the left atrium of the heart. They most often begin in the wall that divides the two upper chambers of the heart. They can occur in other intra-cardiac sites as well. Atrial myxomas are sometimes linked with valve obstruction stenosis and atrial fibrillation.
Myxomas are more common in women. About 1 in 10 myxomas are passed down through families (inherited). These tumors are called familial myxomas. They tend to occur in more than one part of the heart at a time, and often cause symptoms at a younger age.
Symptoms
Many myxomas will not cause symptoms. These are often discovered when an imaging study (echocardiogram, MRI, CT) is done for another reason.
Symptoms may occur at any time, but often they go along with a change in body position.
Symptoms of a myxoma may include:
- Breathing difficulty when lying flat or on one side or the other
- Breathing difficulty when asleep
- Chest pain or tightness
- Dizziness
- Fainting
- Sensation of feeling your heart beat (palpitations)
- Shortness of breath with activity
- Symptoms due to embolism of tumor material
The symptoms and signs of left atrial myxomas often mimic mitral stenosis (narrowing of the valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle). Right atrial myxomas rarely produce symptoms until they have grown to be quite large (5 inches wide, or 13 cm).
Other symptoms may include:
- Bluish skin, especially on the fingers (Raynaud phenomenon)
- Cough
- Curvature of nails accompanied by soft tissue swelling (clubbing) of the fingers
- Fever
- Fingers that change color upon pressure or with cold or stress
- General discomfort (malaise)
- Joint pain
- Swelling in any part of the body
- Weight loss without trying
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam and listen to your heart through a stethoscope. Abnormal heart sounds or a murmur may be heard. These sounds may change when you change body position.
Imaging tests may include:
- Chest x-ray
- CT scan of chest
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Echocardiogram
- Duplex Doppler study
- Heart MRI
- Left heart angiography
- Right heart angiography
You may also need blood tests including:
- Complete blood count (CBC) - may show anemia and increased white blood cells
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) - may be increased
Treatment
Surgery is needed to remove the tumor, especially if it is causing heart failure symptoms or an embolism.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most of the time, surgery can successfully remove the myxoma. Rarely, the tumor may come back after several years. Your provider will likely recommend regular monitoring to check for new myxomas.
Having a myxoma can also increase the risk for heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias) This can be treated with medicines or other treatments.
Untreated, a myxoma can lead to an embolism (tumor cells or a clot that breaks off and travels in the bloodstream). This can lead to a blockage of blood flow. Pieces of the tumor can move to the brain, eye, or limbs.
If the tumor grows inside the heart, it can block blood flow, causing symptoms of obstruction.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Arrhythmias
- Pulmonary edema
- Peripheral emboli
- Blockage of the heart valves
Alternative Names
Cardiac tumor - myxoma; Heart tumor - myxoma
References
Lenihan DJ, Reardon MJ, Hundley WG. Tumors affecting the cardiovascular system. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 98.
Tazelaar HD, Maleszewski JJ. Tumors of the heart and pericardium. In: Fletcher CDM, ed. Diagnostic Histopathology of Tumors. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 2.
Review Date 5/27/2024
Updated by: Michael A. Chen, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Medicine, Division of Cardiology, Harborview Medical Center, University of Washington Medical School, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. Editorial update 11/14/2024.